Key Takeaway:
- Heavy drinking can lead to serious health problems: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to liver disease, heart disease, and cancer, among other health issues. It is important to limit alcohol consumption to prevent these health risks.
- Heavy drinking has negative impacts on mental health: Consuming large quantities of alcohol can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. It can also increase the risk of suicide and other dangerous behaviors.
- Heavy drinking can damage personal and professional relationships: Alcohol abuse can strain relationships with friends, family, and coworkers, and can lead to job loss or other negative consequences. It is important to seek help if you or a loved one is struggling with heavy drinking.
Binge drinking is a prevalent and concerning issue that affects individuals of all ages and backgrounds. In this article, we will delve into the world of binge drinking, discuss the numerous health risks associated with this dangerous behavior, and examine the demographics most affected by binge drinking.
Binge drinking not only puts a person’s physical health at risk, but it also has significant consequences for mental and emotional well-being. From liver damage to alcohol poisoning, binge drinking can have both immediate and long-term effects on one’s health. Furthermore, this excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate mental health issues, impair judgment, and lead to dangerous situations. By understanding the risks and demographics most affected by binge drinking, we can better recognize the warning signs and take steps to address and prevent this harmful behavior in our communities, especially on college campuses, among the elderly, and the working class.
Short-Term Health Risks
Heavy drinking can bring short-term health risks such as dehydration, nausea, vomiting, and bad decision-making.
When too much alcohol is consumed, dehydration occurs, causing dizziness, headaches, and fatigue. Alcohol also irritates the stomach, leading to nausea and vomiting. Plus, it inhibits the ability to think rationally, which can be risky.
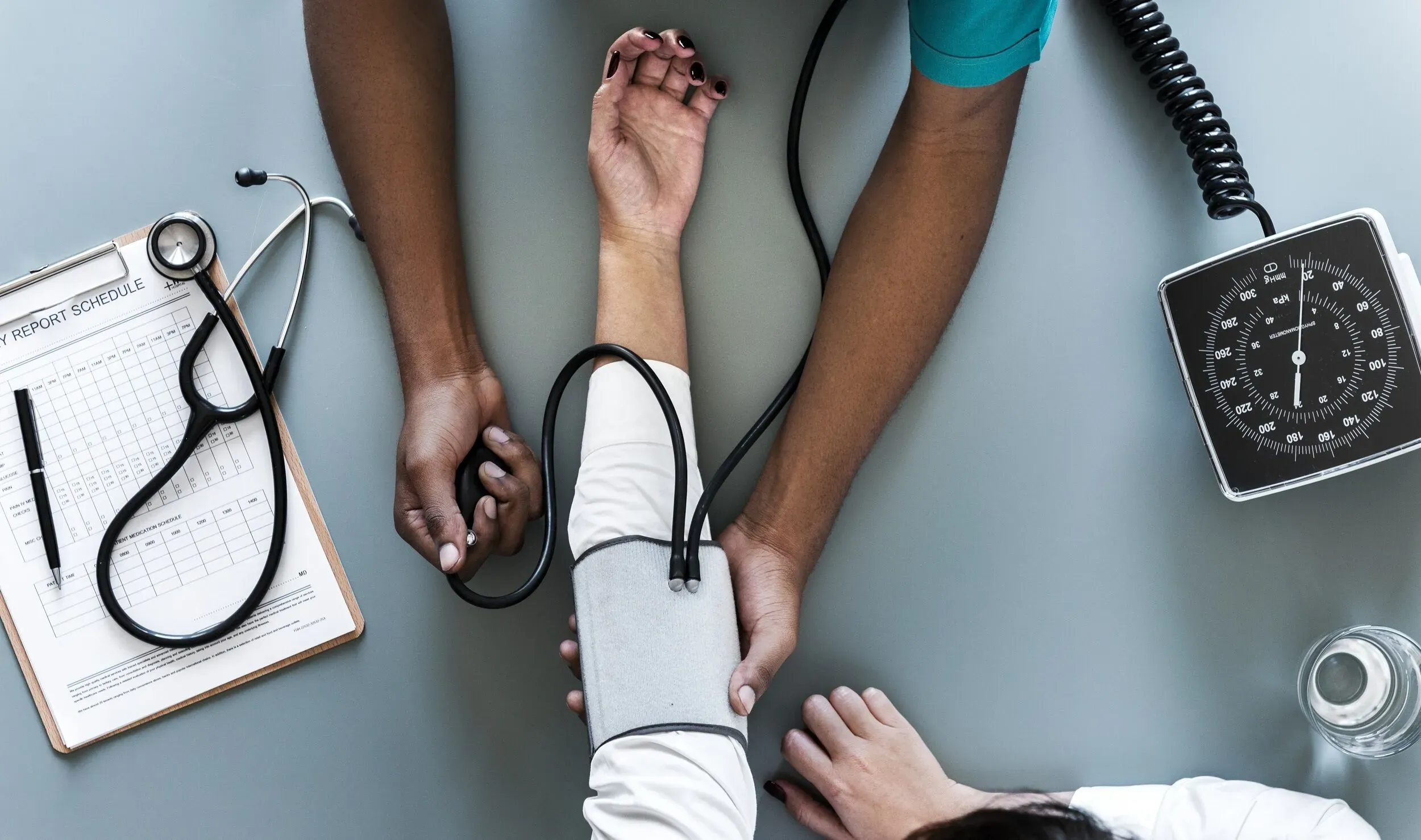
Long-term effects of heavy drinking may include damage to the liver, pancreas, and other organs. Also, it increases the chances of accidents, injuries, and alcohol poisoning.
It’s important to drink in moderation, stay hydrated, and get medical help if severe symptoms occur.
Long-Term Health Risks
Heavy drinking is a major health risk. Long-term alcohol use can harm organs, such as the liver and brain. It can also cause physical and mental health issues. Excessive drinking raises the chance of getting cancer, infertility and heart diseases. Plus, it can lead to malnutrition and weaken the immune system. This makes it harder for the body to fight infections. Alcohol can make pre-existing conditions worse, like high blood pressure and diabetes.
Quitting heavy drinking is hard. Acknowledge the problem and get professional help to start a healthier future. With treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to reduce or remove the risks of heavy drinking.
Health Risks of Heavy Drinking
Heavy drinking can cause many health problems–from mild to severe. Liver problems, like cirrhosis, hepatitis, and fatty liver. Heavy drinking can also cause inflammation of the pancreas, leading to pancreatitis.
Heavy drinking can also lead to brain issues over a long period of time such as memory loss, mood changes, and decreased cognitive function. Heavy drinking has also been linked to cancer risks including liver, throat, and breast cancer. High blood pressure, weakened immune system, and digestive issues. It’s also common for alcoholism to result in long-term mental and social concerns–depression, anxiety, and social isolation.
College Students And Heavy Binge Drinking
According to the University Of Rochester, College Students tend to drink more than their peers who do not attend college. Here are some of the negative health statistics associated with college students and binge drinking.
- 1,825 college students die from alcohol-related unintentional injuries, including motor-vehicle crashes.
- 696,000 college students are assaulted by another student who has been drinking.
- 97,000 college students report an alcohol-related sexual assault or date rape.
Liver Damage
Heavy drinking can damage the liver. This is serious and can even be life-threatening. The liver filters toxins and breaks down alcohol. When a person drinks too much, the liver can’t cope. This leads to inflammation, scarring, and other types of damage.
Symptoms of liver damage are:
- tiredness
- no appetite
- feeling sick
- yellow skin
In bad cases, it can lead to liver failure. This is an emergency and needs medical help.
To keep the liver safe, drink alcohol in moderation or don’t drink at all. Eat healthily and exercise too. If you’re worried, speak with a professional immediately about testing and how to keep your liver healthy.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is a severe and life-threatening condition that can be triggered by heavy drinking. Long-term alcohol misuse can put a huge strain on the heart, causing serious health problems. Research has established that excessive alcohol consumption can increase the chance of high blood pressure, heart failure, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Heavy drinking can produce an irregular heart rhythm, called an arrhythmia. This can weaken the heart muscle over time and result in heart failure. Alcohol is also speculated to raise the triglyceride levels in the blood, which can cause a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
In conclusion, heavy drinking can have destructive effects on the heart and overall wellbeing. It is essential to be aware of the hazards of alcohol abuse and to get help if drinking has become an issue. Adopting a healthy and active lifestyle with moderate drinking habits can reduce the risk of heart disease and other serious health issues significantly.
Brain and Nervous System Damage
Heavy drinking can cause serious harm to the brain and nervous system. Brain cells can’t communicate properly due to alcohol, resulting in motor and cognitive issues. Chronic, heavy drinking can cause permanent changes to the brain’s structure and function.
Alcohol-induced brain harm is a result of oxidative stress, inflammation, and genetic vulnerability. This can lead to anxiety, depression, and dementia.
The peripheral nerves are also damaged by alcohol. This leads to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet. The autonomic nervous system that regulates essential body functions like heart rate and blood pressure is affected too. So, heavy drinkers may suffer from high blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, and heart failure.
Cancer
Heavy drinking is a risk factor for cancer. It can damage DNA, leading to mutations and cell growth. It also makes it harder for the body to remove toxins that can cause cancer.
To reduce the risk, the recommendation is to have no more than one drink per day for women, and up to two drinks per day for men. It is important to remember that too much alcohol can be harmful. People should take steps to limit their drinking and seek help if needed.
Infections
Heavy drinking increases the risk of numerous infections that can be damaging to health. Consuming alcohol excessively weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to illnesses. Common infections linked to heavy drinking include Alcohol-Induced Pneumonia and Tuberculosis, which mostly affects the lungs but can spread to other body parts.
Hepatitis, caused by the inflammation of the liver, can be life-threatening if not treated in time. Septicemia is another deadly infection that can occur due to heavy drinking. It happens when harmful bacteria enter the bloodstream and can lead to Sepsis or Septic Shock, potentially causing multiple organ failure or death.
It is important to drink alcohol in moderation and heed to the warnings of excessive drinking to avoid these dangerous infections.
Binge Drinking and its Dangers
Binge drinking, also known as heavy drinking, is a hazardous action that poses multiple risks to one’s health and wellbeing. When a person gulps down too much alcohol, quickly leading to a BAC level above 0.08, it can cause alcohol poisoning, coma, or even death.
Long-term effects of heavy drinking include liver damage, heart issues, and a greater chance of particular cancers. Also, binge drinking can cause undesirable behaviors like impaired judgment, blackouts, and dangerous situations, which can lead to physical injury or legal problems, and social exclusion.
To stay away from the dangers of heavy drinking, it is advised to reduce alcohol intake to moderate amounts, keep hydrated, eat before or during drinking, and avoid drinking games or peer pressure.
Alcohol poisoning
Alcohol poisoning is when someone drinks too much, leading to a serious level of intoxication. It can be fatal in extreme cases. Heavy drinking is a big cause of alcohol poisoning and can cause physical and mental health problems.
Signs of alcohol poisoning include:
- confusion
- slurred speech
- vomiting
- seizures
- low body temperature
- a fast heartbeat.
If it’s not treated, alcohol poisoning can lead to respiratory failure, coma, or even death.
To avoid alcohol poisoning, it’s important to:
- drink moderately and understand one’s alcohol tolerance
- stay hydrated
- eat before or during drinking
- know when to stop drinking.
Repeated episodes of heavy drinking can increase the risk of developing alcohol dependency, liver damage, and other chronic health conditions.
Physical injuries
Alcohol consumption can raise your risk of physical injuries. Impaired motor skills and coordination can lead to tripping or falling. High levels of drinking can cause drowsiness or even falling asleep.
Alcohol can also impair judgment, driving people to do risky things like driving under the influence. It can also make people more aggressive, leading to violence and other injuries. So, it’s important to drink responsibly and in moderation to protect your safety.

Mental health risks
Heavy drinking presents risks to your mental health, such as depression, anxiety, bad decisions, memory loss and cognitive decline. Alcohol changes the chemicals in your brain that control feelings and emotions, which can cause mental health issues. Plus, drinking too much can lead to memory problems and an increased risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s.
People who have mental health difficulties may be more likely to turn to alcohol as a way to cope. This can start a harmful cycle of self-medication and addiction. If you or someone you know is having mental health problems and is using alcohol, it’s important to get help from a professional. It is essential to understand the dangers of heavy drinking for your mental and physical health.
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is a serious, ongoing illness. Women who drink more than 8 drinks a week and men who drink over 15 drinks per week can develop the disease. It can cause physical, psychological and social troubles.
It can bring on health problems like liver disease, heart issues, cancer and mental illnesses, like depression and anxiety. To prevent an addiction to alcohol, it is important to recognize the warning signs, for instance, a high tolerance for alcohol, withdrawal symptoms without drinking, and ignoring other duties to drink.
Treatment options for alcoholism are counseling, medication-assisted treatment, and help from groups like Alcoholics Anonymous. It is also noteworthy that, even though moderate drinking may have some health advantages, heavy drinking and alcoholism are linked with dangerous health risks and must be avoided.
Effects of Alcohol on Developing Brain
Drinking too much during teenage years or early adulthood can be bad for the growing brain. It can cause problems with attention, memory and learning, meaning it may affect school or social life. It can also stop brain cells from growing and communicating properly.
Excess alcohol use during this time can put you at risk for long-term health issues. It can change your mood, and studies have shown that heavy drinking early in life can mean more problems with anxiety and depression later.
Plus, drinking before the brain is fully grown can make it more likely to become dependent on or addicted to alcohol. It’s important to educate teenagers and young adults about the risks of drinking too much and to take steps to stop it. If you or someone you know has an alcohol problem, talk to a doctor or addiction expert.
Disease and Injury Conditions Associated With Alcohol Use
Long-term, heavy drinking can be detrimental to your health. It increases the risk of developing certain diseases. These include:
- Cancer – such as breast, liver, colon and throat cancer.
- Liver Disease – cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis and fatty liver disease.
- Cardiovascular Disease – high blood pressure, stroke and heart attack are all linked to excessive drinking.
- Brain Damage – memory loss, cognitive impairment and neuropathy can all be caused by heavy drinking.
- Mental Health Issues – anxiety, depression and other mood disorders can be made worse due to alcohol use disorder.
It is important to be aware of these potential long-term consequences and reduce your alcohol intake in order to stay healthy.
Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Consuming more than four drinks a day or eight drinks a week can significantly raise the chance of having neuropsychiatric disorders. These disorders affect emotions and thinking.
Studies have shown heavy drinking can make anxiety levels higher in both men and women. Symptoms like restlessness and irritability may follow. It has also been linked to depression. People who drink heavily often have depressive episodes.
Heavy drinking can also impair cognitive functions. Memory, learning, and decision-making can suffer. Over time, it can cause permanent brain damage and increase the risk of dementia.
It is essential to limit alcohol intake to safe levels and get help if addiction is a problem.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Heavy drinking can lead to heart problems. It raises blood pressure and weakens heart muscles. These are some of the ways it can cause cardiovascular diseases:
- High blood pressure: Drinking makes pressure greater, straining the heart and vessels.
- Atrial fibrillation: Drinking increases the risk of irregular heartbeat, which can cause clots, stroke, and heart failure.
- Cardiomyopathy: Drinking makes the heart muscles rigid, leading to heart failure and other issues.
- Coronary heart disease: Drinking leads to plaques in the arteries, causing coronary heart disease and heart attacks.
To avoid these risks, limit alcohol and live a healthy life.
Diseases of the Liver and Pancreas
Heavy drinking can be detrimental. It can cause damage to the liver and pancreas. This can lead to various, potentially fatal, diseases. Cirrhosis is one such liver disease. It is marked by the formation of scar tissue in the liver. This can cause liver failure and raise the risk of liver cancer. Pancreatitis is another serious condition. It occurs when the pancreas becomes inflamed. This makes it hard to break down food and produce insulin, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
To prevent these alcohol-related diseases, limit alcohol consumption. Eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly. If any symptoms of liver or pancreatic disease are noticed, seek medical treatment quickly. These diseases can worsen rapidly and have dire consequences.
Unintentional Injuries
Heavy drinking? Not a good idea! It can lead to unintentional injuries like falls, burns and traffic crashes. These come from impaired balance, coordination, and reaction time.
- Falls from stairs, balconies, and wet surfaces.
- Fires, cigarette burns, and traffic accidents.
All of these are potential risks of heavy drinking. Research has proven this to be one of the leading causes of preventable injury-related deaths globally.
Under the influence, people cannot always control their actions. This leads to situations where they can get injured or killed. So, the CDC recommends responsible drinking and designating a driver or use other transportation options when drinking.
Intentional Injuries
Intentional injuries due to heavy drinking are a real worry. Alcohol can cause foggy judgment and a lack of control. This can cause dangerous scenarios and bad decisions. Binge drinking and too much alcohol can trigger assaults, self-harm, and suicide attempts resulting in alcohol abuse.
- Alcohol can worsen aggressive behavior and make bad decisions more likely.
- People with an alcohol dependency or addiction are especially vulnerable to intentional injuries. Their judgment and control of impulses may be badly affected.
It’s essential to seek help and treatment for alcohol addiction to stop more intentional harm and improve overall health.
Social Harm of Heavy Drinking
Heavy drinking, or alcohol abuse, can have serious social consequences. It can harm the drinker and their loved ones, not just physically. This can cause:
- Problems in relationships with family, friends, and partners. It can increase stress and tension.
- Financial issues due to high spending on alcohol. It can also lead to job loss or low productivity.
- Stigmatization and social discrimination leading to isolation and poor mental health.
- Negative impacts on academic and professional goals. Poor decision-making and absenteeism can be a result.
In conclusion, heavy drinking can have major and long-lasting social harm. It affects the individual and their family, friends, and community. Seeking support to find out the severity of your drinking problem is key to recovering to a normal, healthy life.
Getting Help for Heavy Drinking
Help for heavy drinking is vital. It involves drinking lots of alcohol often, and has many problems it can cause. These involve:
- Liver damage. This can become hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis and even liver failure.
- Alcohol poisoning. It can lead to seizures, difficulty breathing and coma or death.
- Impaired judgment. This can mean drunk driving and accidents.
- Relationship problems. Drinking too much can mean family, friends or partners becoming distant or isolated.
If you, or someone you know, is battling heavy drinking, don’t delay. There are lots of resources, such as rehab, help groups and counseling. It’s never too late to get help and change your life. Additionally, these intervention strategies may give a headstart to your loved ones’ new beginning.
Five Facts About The Dangers of Heavy Drinking:
- ✅ Heavy drinking can increase the risk of liver disease, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. (Source: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism)
- ✅ Overconsumption of alcohol can lead to high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. (Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- ✅ Drinking heavily over a prolonged period can impair brain function, including memory loss, difficulty with coordination and balance, and a greater risk of dementia. (Source: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism)
- ✅ Alcohol misuse can cause damage to the digestive system, leading to problems such as gastritis and pancreatitis. (Source: Mayo Clinic)
- ✅ Heavy drinking can increase the risk of several types of cancer, including breast, liver, mouth, and throat cancer. (Source: Cancer.net)
FAQs about The Dangers Of Heavy Drinking
What are the dangers of heavy drinking?
Heavy drinking can lead to a variety of health problems, such as liver disease, high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and cancer. It can also impair your judgment and coordination, leading to accidents and injuries, and increase your risk of engaging in risky behaviors like unprotected sex and driving under the influence.
How much alcohol is considered heavy drinking?
For men, heavy drinking is defined as consuming more than four drinks in a day or 14 drinks in a week. For women, heavy drinking is defined as consuming more than three drinks in a day or seven drinks in a week.
How does heavy drinking affect mental health?
Heavy drinking can increase your risk of developing mental health issues like depression and anxiety, and can also worsen existing conditions. It can also lead to memory loss and cognitive impairment.
Can heavy drinking be fatal?
Yes, heavy drinking can lead to alcohol poisoning, which can be fatal. It can also increase your risk of accidents and injuries that can be life-threatening.
How can I tell if someone is struggling with heavy drinking?
Signs that someone may be struggling with heavy drinking include a high tolerance for alcohol, frequent alcohol consumption, neglecting responsibilities, social isolation, mood swings, and physical symptoms like tremors and nausea.
What are some ways to reduce my risk of heavy drinking?
Limiting your alcohol consumption, avoiding binge drinking, and seeking help if you feel that you cannot control your drinking habits are all ways to reduce your risk of heavy drinking. It can also be helpful to develop healthy coping mechanisms and find alternative ways to deal with stress, anxiety, and other difficult emotions.
More Information on Alcohol Use Disorder
- 10 Signs Of Having A Drinking Problem
- Risks Of Binge Drinking
- Treatment For Alcohol Use Disorder
- Impacts Of Alcohol Abuse On The Brain
- How Long Does Alcohol Stay In Your System?
- Different Types Of Drinkers
- Alcohol Abuse And Links To Dimentia
- Does Alcoholism Run Families?
- What To Look For In A Developing Alcoholic