Navigating the intricacies of drug testing can feel like a daunting puzzle, especially when it comes to substances like ketamine. Whether you’re a responsible user seeking to ensure a clean drug test or simply curious about the duration ketamine lingers in your body, understanding its presence in the system becomes paramount.
This article will explore everything about ketamine’s stay within the body and its detectability in drug tests. Delving into the intricate interplay of dosage, frequency of use, metabolism, administration routes, individual characteristics, and various testing methods, you’ll be equipped with the insights needed to navigate the intricate web of drug testing successfully.
What is Ketamine?
Ketamine is a medication that has both anesthetic and hallucinogenic properties. It was first developed in the 1960s as an anesthetic agent, primarily used in veterinary medicine. However, it has also been used in human medicine for anesthesia in certain situations, particularly in emergency and battlefield settings.
Ketamine is classified as a dissociative anesthetic because it can induce a trance-like state where the person may feel detached from their surroundings, experience a distortion of time and space, and have hallucinations. These effects are sometimes described as a “K-hole” experience.
In addition to its anesthetic properties, ketamine has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic uses. Research has suggested that ketamine may have rapid-acting antidepressant effects and may be effective in treating treatment-resistant depression. It is administered in controlled settings, usually as an intravenous infusion, under the supervision of healthcare professionals.
Ketamine is a controlled substance due to its potential for misuse and recreational use. When used recreationally, it is often referred to as “Special K” or simply “K,” and it can be associated with significant health risks and adverse effects. Misuse of ketamine can lead to psychological dependence and other negative consequences.
How Long Does Ketamine Last in Your System?
The duration that ketamine remains detectable in the body can vary depending on several factors, including the dose taken, the frequency of use, the individual’s metabolism, and the type of drug test being conducted. Here are some general guidelines:
- Blood: Ketamine can typically be detected in blood tests for up to 48 hours after use.
- Urine: Ketamine and its metabolites can be detected in urine for a longer period compared to blood. It is generally detectable for up to 3-6 days after use. However, heavy or chronic use may extend the detection window.
- Saliva: Ketamine can be detected in saliva for approximately 1-2 days after use.
- Hair: Ketamine can be detected in hair follicles for a longer duration compared to other testing methods. It can be detected in hair for several months to years after use, depending on the length of the hair sample collected.
The drug detection times listed above are approximate, intended as general guidelines and can vary based on individual factors. Additionally, drug tests may not specifically target ketamine, and its detection may depend on the test’s sensitivity and the purpose of the screening.
What are the Factors That Affect How Long Ketamine Stays in Your System?
Some of the factors that could affect the duration of Ketamine in your body can include, but are not limited to the following:
1. Dosage
The amount of ketamine taken can affect the drug’s elimination time. Higher doses may take longer to clear from the body compared to lower doses.
2. Frequency of use
Regular and repeated use of ketamine can lead to its accumulation in the body over time. This can result in an extended detection window as the drug takes longer to be metabolized and eliminated.
3. Metabolism
The rate at which your body metabolizes ketamine can vary from person to person. Factors such as age, liver function, and overall metabolism can influence how quickly ketamine is broken down and eliminated from the body. Individuals with a faster metabolism may eliminate the drug more rapidly.
4. Route of administration
Ketamine can be administered through various routes, including intravenous (IV) injection, intramuscular (IM) injection, oral, and intranasal. The route of administration can affect the absorption, distribution, and elimination of the drug, which in turn can impact how long it remains in your system. For example, intravenous administration may result in a quicker onset of effects and faster elimination compared to oral administration.
5. Body composition
Body fat percentage and overall body mass can influence the distribution and elimination of drugs. Ketamine, like many other drugs, tends to accumulate in fatty tissues. People with higher body fat percentages may retain ketamine for longer periods compared to individuals with lower body fat percentages.
6. Individual factors
Each person’s unique physiology and genetic makeup can affect drug metabolism and elimination. Genetic variations in drug-metabolizing enzymes can impact how quickly ketamine is broken down and cleared from the body.
Note that these factors interact with each other, leading to changes in duration. Additionally, the duration of ketamine’s presence in the body can vary significantly from person to person.
How Long Do the Effects of Ketamine Last?
The duration of the effects of ketamine can vary depending on several factors, including the dose taken, the route of administration, and individual differences. Here are some general guidelines for the duration of ketamine’s effects:
- Intravenous (IV) administration: When ketamine is administered intravenously, the effects are typically felt within seconds to minutes, and they can last for about 30 minutes to an hour. This is the fastest-acting route of administration.
- Intramuscular (IM) injection: With IM injection, the effects of ketamine usually begin within a few minutes and can last for approximately 45 minutes to 2 hours.
- Oral administration: When taken orally, the onset of ketamine’s effects is generally slower compared to injection methods. It can take around 20 to 30 minutes for the effects to be felt, and they may last for 1 to 3 hours.
- Intranasal administration: Ketamine can also be administered by nasal spray or as a powder insufflated through the nose. The effects typically start within a few minutes and may last for about 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
The duration of ketamine’s effects can be influenced by factors such as individual sensitivity, the presence of other substances in the body, and the specific formulation and purity of the drug.
Additionally, at lower doses, ketamine may induce a state of relaxation, pain relief, and mild dissociation. At higher doses, it can produce more profound dissociative and hallucinogenic effects, which may include a sense of detachment from one’s body and surroundings, visual and auditory distortions, and a loss of a sense of time and identity.
What is Withdrawal From Ketamine Like?
The withdrawal symptoms associated with ketamine can vary in intensity and duration depending on several factors, including the frequency and duration of use, the dosage, and individual factors. However, it’s important to note that ketamine withdrawal is generally less severe compared to withdrawal from substances like opioids or benzodiazepines.
Here are some common withdrawal symptoms that may occur when discontinuing or reducing ketamine use:
1. Psychological symptoms
These may include mood swings, anxiety, irritability, depression, restlessness, and cravings for ketamine. Some individuals may also experience difficulty concentrating and sleeping.
2. Physical symptoms
Physical withdrawal symptoms from ketamine are generally milder compared to other substances. They may include mild tremors, increased heart rate, sweating, and changes in appetite.
3. Cognitive symptoms
Ketamine withdrawal can sometimes lead to cognitive difficulties, such as problems with memory, attention, and decision-making. These effects are usually temporary and tend to improve over time.
Ketamine withdrawal symptoms are generally milder and of shorter duration compared to substances with more severe withdrawal syndromes. The onset and duration of withdrawal symptoms can vary among individuals. Some individuals may experience minimal or no withdrawal symptoms, while others may have more pronounced symptoms.
If you or someone you know is experiencing ketamine withdrawal symptoms or is struggling with ketamine use, it is important to seek medical help and support. A healthcare professional or addiction specialist can provide guidance, support, and appropriate treatment options.
What is the Half-Life of Ketamine?
The half-life of ketamine can range between 2.5 to 3 hours when administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM). This means that after the initial dose, it takes approximately 2.5 to 3 hours for the concentration of ketamine in the body to decrease by half.
The half-life of ketamine can be influenced by several factors, including the dose administered, the individual’s metabolism, and the presence of other medications or substances. Additionally, the half-life can be different for the various metabolites of ketamine, as they may have different rates of elimination from the body.
What are the Side Effects of Ketamine Abuse?
Abusing ketamine, particularly when used in higher doses or in a recreational context, can lead to various side effects. These side effects can vary in severity and may include:
1. Cognitive and psychological effects
Ketamine abuse can cause confusion, disorientation, memory loss, and difficulties with attention and concentration. It can also induce hallucinations, delusions, and a distorted sense of reality. Some individuals may experience mood swings, anxiety, panic attacks, and even symptoms resembling psychosis.
2. Physical effects
Ketamine abuse can lead to physical symptoms such as dizziness, blurred vision, increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and impaired coordination. It can also cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. In some cases, individuals may experience a loss of sensation or numbing in different parts of the body.
3. Urinary and bladder problems
Long-term and heavy ketamine abuse can result in a condition called ketamine-induced cystitis. This condition is characterized by inflammation and damage to the bladder, leading to symptoms such as frequent urination, pain during urination, blood in the urine, and difficulty controlling urination.
4. Dependence and addiction
Ketamine has the potential for psychological dependence and addiction. Prolonged and frequent abuse of ketamine can lead to tolerance, where higher doses are needed to achieve the desired effects. This can increase the risk of addiction, making it difficult for individuals to stop using the drug despite negative consequences.
5. Other risks
Ketamine abuse can increase the risk of accidents and injuries due to impaired judgment, coordination, and perception. It can also lead to risky behaviors and poor decision-making. Combining ketamine with other substances, such as alcohol or sedatives, can amplify the risks and potential side effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the duration that ketamine stays in your body varies based on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, metabolism, route of administration, body composition, and individual factors.
Detection times in blood, urine, saliva, and hair tests range from hours to months. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate information. Responsible use of ketamine is crucial to avoid adverse effects on health.










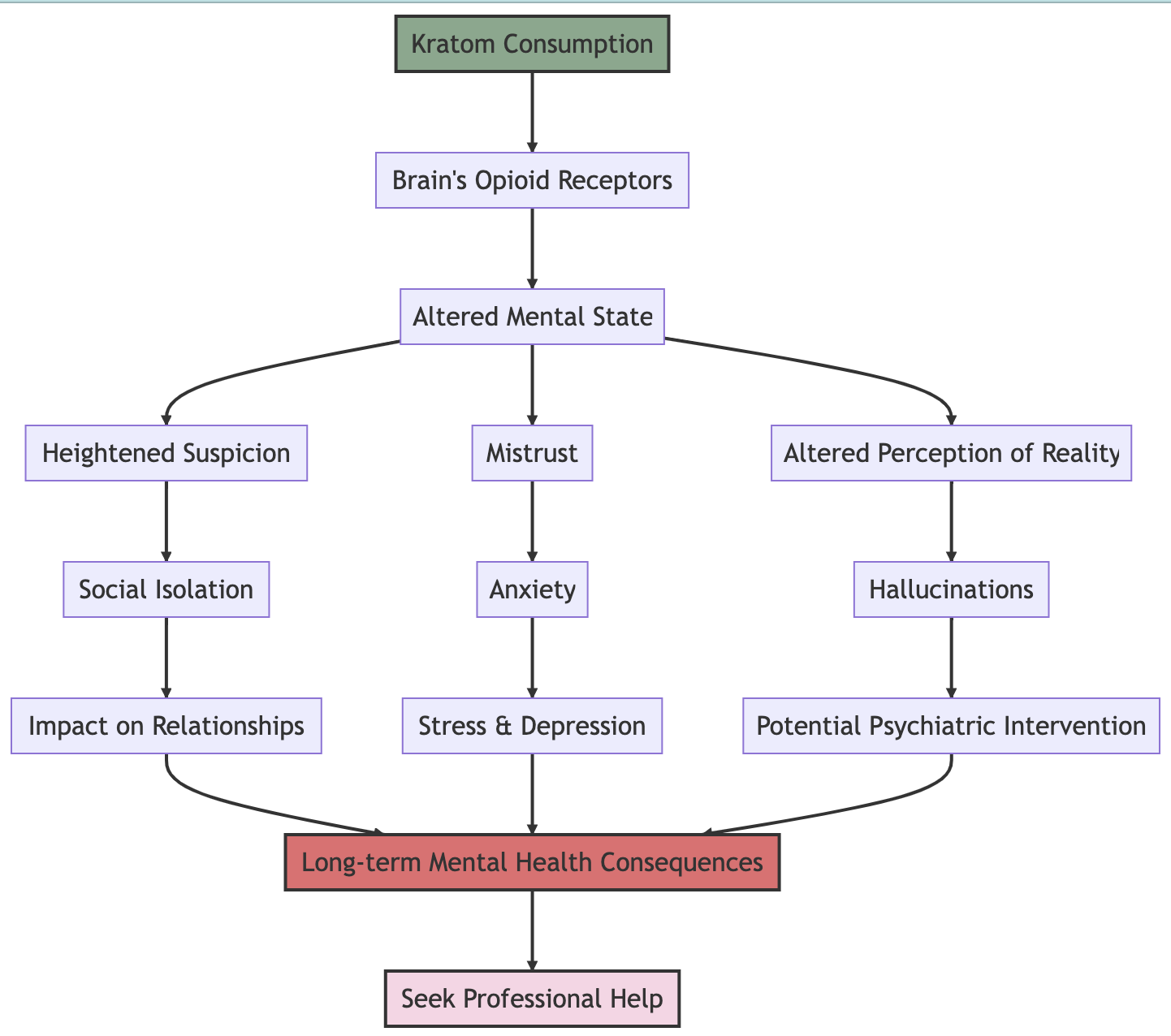
 Easy to obtain and use: The leaves of the kratom plant are chewed or ground up and dissolved in drinks. The effects of this substance usually occur within 5 to 10 minutes of ingestion, and may last for 2 to 5 hours. Kratom is extremely easy to buy over the counter which makes it a risk for youth and other individuals that are not aware of the side effects that can result from its use.
Easy to obtain and use: The leaves of the kratom plant are chewed or ground up and dissolved in drinks. The effects of this substance usually occur within 5 to 10 minutes of ingestion, and may last for 2 to 5 hours. Kratom is extremely easy to buy over the counter which makes it a risk for youth and other individuals that are not aware of the side effects that can result from its use.